Gingivitis is considered the beginning of gum disease. It causes inflammation of tissues supporting and covering the teeth and poor hygiene is the main cause of this problem. It is a very prevalent condition and its severity varies. Red, swollen gums which bleed when you floss or brush your teeth are the main signs of gingivitis. But periodontitis is a different thing. Gingivitis acts as a sign of warning behind periodontitis, which is a more serious condition.
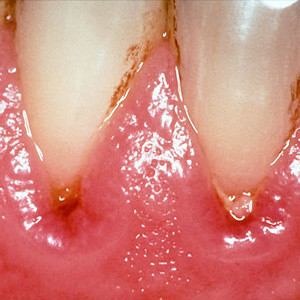
Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis
Gingivitis occurs due to inflammation of gums covering the teeth. On the other side, periodontitis is an infection of bone below the gums. Periodontal refers to ‘around the teeth’ and the structures covering and supporting teeth like bone and gums.
When food leftovers mix with bacteria and saliva which form plaque to the teeth surface, gingivitis starts developing. If plaque is not removed by flossing and brushing, it causes tarter and gets mineralized. Tarter can be removed only by a professional dental cleaning.
Both tarter and plaque are loaded with bacteria. If they are not removed, they start causing gum problems and later gum disease. Due to the lack of treatment, gingivitis starts extending to the bone and causes periodontitis. Due to infection of the bone, deep gum pockets are formed. They constantly build up bacteria and plaque. These pockets are very tough to clean up and they cause more loss of bones. As this problem goes to the advanced stage, it causes further loss of bone tissues. As a result, gum pockets get deeper and, in the end, teeth start falling.
What are the Causes?
Poor oral hygiene is the main cause of bacteria buildup in calculus and plaque on the teeth and gum infection is the main cause of gingivitis. Here are some of the other risk factors –
- Chewing or smoking tobacco prevents healing
- Rotated, crooked or overlapping teeth create more calculus and plaque to build up and are not easier to keep clean
- Hormonal changes in menopause, puberty, and pregnancy
- Cancer and cancer treatment
- Stress
- Alcohol influence
- Poor nutrition like a diet high in carbs an sugar
- No or poor dental care
- Low saliva production
- Medications like anti-seizure
What are the signs and symptoms?
- Swollen, bright red gums which bleed constantly, even during flossing or brushing
- Constant mouth odor or bad taste
- Plaque or white spots on gums
- Pus between inter-dental spaces or gums
- Tooth loss or loose tooth
- Changes in how partial dentures fit
Diagnosis
- Measuring Gums – A dental hygienist or dentist uses a probe to measure the pockets’ depth around the teeth, at least once in a year. Healthy gums have 1mm to 3mm deep pockets. If they are deeper, the disease gets severe.
- X–Rays – Dental x-rays show the level of bones and whether there is a loss of bone due to the periodontal problem.
- Determining sensitive teeth – Sensitive teeth across the gum line may show areas of gums.
- Checking the gums – A dentist will look for swollen, red or bleeding gums.
- Checking for loose teeth – Teeth can get loose because of improper bite or bone loss.
Gum Treatment
The main goal of gum treatment is to determine and eliminate factors causing gum disease. With professional dental cleaning and proper and regular oral hygiene, you can avoid most of the common problems. After removing the plaque and tartar, a dentist helps the patient to avoid gingivitis and recommends flossing and brushing after having every meal. They may recommend a mouth rinse which addresses oral bacteria causing gum disease.
